Europe was alight with speculation on Friday about verdicts on the financial health of the region’s 130 largest lenders.
Europe was alight with speculation on Friday about verdicts on the financial health of the region’s 130 largest lenders.
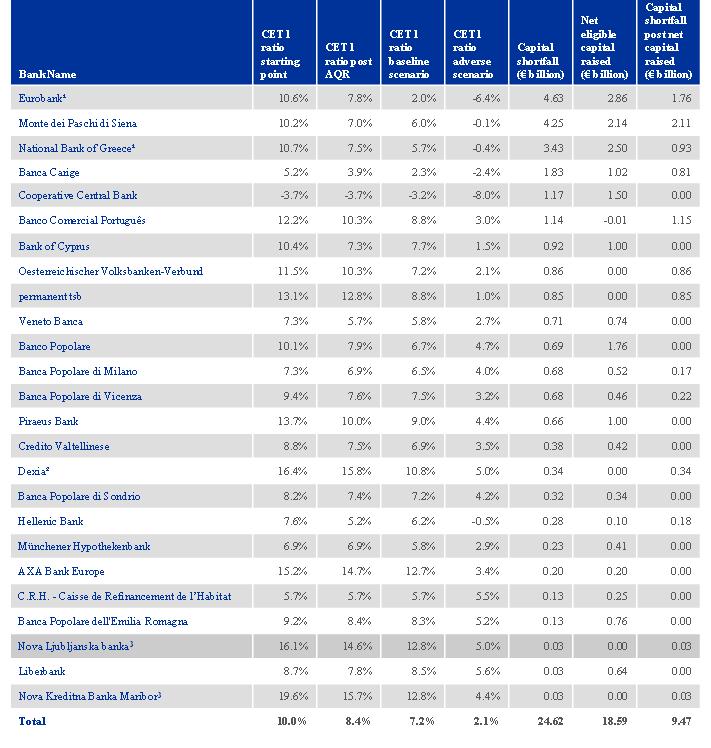
The big question was - and, well 25 failed - which banks might fail the central bank’s review and how much new capital might be needed for the banks to survive. Estimates of the capital shortfall varied widely, from about 10 billion euros, or about $12.6 billion, to as much as €50 billion. The central bank’s review was based on figures at the end of 2013. Banks that have not passed muster and have not taken steps to shore up their finances will have nine months to top up their reserves. Otherwise, they risk being shut down. The central bank noted the results would not be final until approved by its governing council Sunday morning. “Until that time, any media reports on the outcome of the tests are by their nature highly speculative,” it said. Banks were informed of the preliminary results of the review and stress tests on Thursday. They will not know for sure whether they passed or failed until Sunday, shortly before the public disclosure. Most analysts expected the shortfall to be relatively modest, in part because bankers have known for a year that the test was coming and have sold risky assets and raised more capital, money that is available to absorb losses and is crucial to a bank’s survival in a crisis. “The number of banks that would need to raise additional capital will be limited,” analysts at Barclays said in a note to clients on Friday. “This is due to the substantial pre-emptive measures that the banks have already undertaken.” Betting on which banks would do better or worse than expected was rampant on Friday. Trading was suspended on Friday in shares of the Italian bank Monte dei Paschi di Siena after they jumped more than 10 percent on the strength of speculation that it would fare better than expected under European Central Bank scrutiny. The larger question is whether the review, which included an audit of bank holdings followed by so-called stress tests of their ability to withstand a crisis, will remove doubts about the underlying health of eurozone lenders and make it easier for them to raise money that they can lend to customers.
Jörg Krämer, chief economist at Commerzbank in Frankfurt, was pessimistic about the effect that the review would have on the eurozone economy. The reason for declining credit in the eurozone is not that banks cannot lend, he said on Friday, but that businesses do not want to borrow. “The stress tests will help certain countries like Italy and Spain,” Mr. Krämer said in a meeting with a small group of journalists. “But it won’t be a breakthrough for the whole eurozone.” There could be a sell-off in financial markets on Monday if the central bank uncovers a bigger capital gap than expected. But there is also a risk of a negative market reaction if the review appears to be too lax. Previous stress tests by other regulators gave stamps of approval to banks that later failed, undermining trust in the whole banking system. The European Central Bank has a strong incentive to be tough. It will become the overall supervisor of eurozone banks on Nov. 4, and needs to show it has the skills and backbone to do the job. “If convincing enough, the assessment can support sentiment, the eurozone economy and the banks,” Suvi Kosonen, an analyst at ING Bank, said in a note on Friday.
The central bank conducted the stress tests with the European Banking Authority, which will simultaneously release results on Sunday that include lenders in European Union countries that are not in the eurozone, like Britain and Sweden. Banks found short of capital will have two weeks to submit a plan to the central bank on how they will shore up their finances. Even banks that pass could find themselves under pressure to raise more capital, if they pass only narrowly. The audit will expose that banks may have been overvaluing their assets or failing to set aside enough money to cover bad loans.(source NYT)
 The "Entrepreneurs" provide us with critical innovation and keep us at the forefront of global markets and they also create ways (for individuals)to gain financial independence. So why has the percentage of start-ups in the U.S. dropped significantly in the last 35 years? This is particularly worrisome in light of the healthy state of the stock market and the many new ways to raise capital. Without the impetus of more business formation, how will we ever lift up the 40 million people currently living below the poverty line... I think there are three factors contributing to the decline of entrepreneurship. For starters, the slow recovery of the economy and stagnant wage levels have caused widespread risk aversion, especially among millennials. With a trillion dollars of college debt weighing them down, they seek the security of a paycheck, even if the pay is low. While a majority (55%) hopes to start a business one day, their dreams remain on hold.
The "Entrepreneurs" provide us with critical innovation and keep us at the forefront of global markets and they also create ways (for individuals)to gain financial independence. So why has the percentage of start-ups in the U.S. dropped significantly in the last 35 years? This is particularly worrisome in light of the healthy state of the stock market and the many new ways to raise capital. Without the impetus of more business formation, how will we ever lift up the 40 million people currently living below the poverty line... I think there are three factors contributing to the decline of entrepreneurship. For starters, the slow recovery of the economy and stagnant wage levels have caused widespread risk aversion, especially among millennials. With a trillion dollars of college debt weighing them down, they seek the security of a paycheck, even if the pay is low. While a majority (55%) hopes to start a business one day, their dreams remain on hold.